Optimization of the repair service as a necessary condition for operational efficiency. The program of accounting equipment, inventory, repairs and services. Program for service centers and repair shops
Country Support:
Operating System: Windows
Family: Universal Accounting System
Appointment: Business automation
Repair Program
Key features of the program:
We have completed business automation for many organizations:
Language of the basic version of the program: RUSSIAN
You can also order the international version of the program, into which you can enter information in ANY LANGUAGE of the world. Even the interface can be easily translated independently, since all the names will be taken out in a separate text file.
A universal accounting system (hereinafter USU), is engaged in the development of specialized software for all types of your business. And in this essay it will be described in detail how the computer program for repair, maintenance in the service center or repair shop will help your business go uphill. So, let's begin.
Firstly, repair control software and maintenance for repair in the workshop will never forget anything, since the data for production repair control is always entered into the system. As for the client base, the program of registration and control thereof will always keep it at hand, and in an optimized way.
Secondly, the USU, as an application for repairs, and as a repair management, will help you with paperwork, because the system contains such documents as: acceptance certificate, warranty card, certificate technical condition, receipt for payment, certificate of completion, etc. The program automatically monitors all areas of your enterprise, making total control of repairs, starting with various financial reports and ending with the management of equipment repairs.
And thirdly: the program for accounting for repairs, control and planning of work in production will help you not only to keep all automated information in one place, but also to improve and organize the production process itself.
And now we will describe the program itself on the system of planning and repair management. The repair registration system starts as standard, i.e. from the desktop shortcut, and then the login window appears. Each user must enter their username and password. Also, each employee can have individual rights to access the management program to see only the information that his authority implies. An automated program can also share information for a director, manager, or a simple worker, which is very convenient and does not create confusion when using an accounting system. All applications that have ever been accepted remain in the archive of the system, which is very convenient when re-contacting your organization, or when returning illiquid goods to the workshop. USU can conduct an automated search by keywords, by individual number, customer name or order features, which reduces the time to search for an application and leaves more time for work. A service accounting will help to distribute new incoming applications by urgency, volume or any other filter of your choice.
All the features of personnel management will recede into the background, as you yourself will see the positive or negative dynamics of work, and then make a decision that optimizes your organization. Based on the data obtained, you can track the work of employees, pay wages with the piecework concept, or the company's profit on each sale.
The repair management system will allow you to track all breakdowns and equipment replacement, which will greatly facilitate the monitoring of both working and to be replaced equipment. Automation of service accounting, repair shops, or software for repair is an advantage both in the competent organization of business functioning and in the status in which a positive attitude of customers and companies cooperating with you is formed.
The control and management program can be used by:
- Authorized service center;
- Combine Technology Center;
- Service center;
- Service company;
- Service-center;
- Atelier workshop;
- Workshop;
- Repair shop;
- Repair company;
- Repair company;
- Trading and service company;
- etc.
After watching the following video, you can quickly get acquainted with the capabilities of the USU program - Universal Accounting System. If you don’t see the video uploaded to YouTube, be sure to write to us, we will find another way to show the demo!
Repair control and management capabilities
- Automation for accounting of a repair shop and repair management is distinguished by an easy menu.
- Organization reporting management and control becomes simpler with the “Reports” program function
- The “Import” and “Export” functions in the program allow you to convert files.
- Working in Modules makes managing a service center fast and efficient.
- Control over all the work done is easily carried out with the help of analytics.
- Searching for data in the program becomes almost lightning fast.
- Switching to other program tabs to account for repair management does not require unnecessary movements.
- Accounting: the management function will create a positive image of the organization;
- You will not need to carry out activities to improve personnel management, as the multifunctionality of the system will allow full control over the actions of personnel and payroll;
- A convenient interface will make data management an easy and affordable process;
- Planning and control are easily feasible using data analysis of financial statements;
- Development of automation systems is our lifestyle. We are honored to offer you a high quality product;
- The system of labor incentives in the organization can be built using the program;
- Quality and performance indicators will always be in the public domain for employees with a code;
- Maintaining a repair business and managing it through an automation program has never been so convenient.
- The withdrawal of the logo and company contacts for all accounting statements.
- Convenient grouping of data by selected automated accounting.
- The floating menu opens up more features of the program.
- Accounting and audit are carried out in two convenient ways.
- The customer base will never fail.
- Accounting for repair control will display all existing and completed orders.
- The program for accounting and management of automated control over the service center operates smoothly and without failures.



After opening the workshop, the question arises about the accounting program in the service center, since with a large flow of customers it is very easy to forget or confuse something.
Requirements for the program for the repair shop:
- Maximum simplicity
- Storage of order and customer data during the warranty period
- The ability to print acts of acceptance and delivery of equipment from repair
- Ability to print reports for the selected period
- Automation to speed up data entry (drop-down lists for a set of standard values \u200b\u200b- device type, manufacturer, etc.)
Overview of programs for service centers and repair shops
Of everything found on the Internet, not a single program came up to us. The problem is that developers rarely use their creations themselves. Somewhere there are simply no reports, somewhere they are printed by the date of issue. Somewhere the price of spare parts is indicated directly in the act of issue. Most programs are bulky, confused and do not satisfy the requirements above. We even came across an online service with a monthly fee.
Own program for a service center for repairing computers, laptops, phones, etc.
As a result, after exhausting torment, I managed to transfer all the advantages of the programs found to a self-written program for the service center. She will arrange many small workshops and will not need any modifications. If changes are needed - I can modify it to order.
Download a free program for service centers
Download Demo Full VersionPlease note that at the first start, the antivirus scans the program and data may not be saved due to the test mode in the sandbox. After that, the antivirus adds the program to the checked ones and everything works fine. Therefore, it is recommended to restart after the first start of the program. In case of problems in the program, add it to the antivirus exceptions.
Support, partnership and custom service program development
In case of problems write to e-mail This email address is being protected from spambots. You must have javascript enabled to view it. . Before writing, just try to add the program folder to the antivirus exceptions. There were cases of testing mode for some antiviruses in the sandbox at the first start of the program, due to which the data was not saved to the database. After restarting the computer or adding the folder with the service program to the exceptions, the problem disappeared.
The solution "1C: MRO Repair and maintenance of equipment 2 KORP" is intended to organize a system for managing repairs and maintenance of equipment at enterprises of various industries, including subject to the requirements of the ISO 55000 asset management standard. The solution belongs to the class of EAM-systems (Enterprise Asset Management - management of fixed assets and enterprise assets).
The solution is intended for employees of the following departments:
- Service chief mechanic.
- Service of the chief power engineer.
- Instrumentation.
- Metrology Service.
- Department of material and technical support (supply).
- Bookkeeping.
- APCS.
The main business processes automated using "1C: MRO Maintenance and repair of equipment 2 KORP":
- Accounting for equipment and standards: collection and maintenance of information on the equipment of the enterprise, its characteristics, repair and maintenance standards, as well as its provision to other MRO processes.
- Performance Management to collect, store and analyze information about the technical condition of equipment during its operation.
- Planning maintenance and repairs: ensuring the proper safety of equipment in the long term, maintaining the normative level of its technical condition and performance.
- Maintenance logistics management of repairs: meeting the needs of enterprises in spare parts (aggregates, units and parts), materials, tools and equipment.
- Personnel Management: determination of the number of necessary repair and maintenance personnel involved in maintenance and repairs.
- Management of orders and work: formation and accounting of the execution of work orders for repair work, if necessary, the formation of work orders, tolerances for them, as well as control of the degree of completion repair work and accounting of performed maintenance and repairs.
- Document Management: consolidation and storage of an electronic archive of documents (drawings, diagrams, etc.) providing repair service personnel with quick access to the necessary documents and equipment repair history.
- Analysis of the effectiveness of the use of enterprise assets and reporting on a different focus.
Solution functionality"1C: TOIR Management of repairs and maintenance of equipment 2 CORP"
Accounting for equipment and standards
· Maintaining a list of equipment.
· Accounting for equipment movements.
· Classification of equipment.
· Maintaining a classifier of normative maintenance and repairs.
· Maintenance of technological maps of repairs.
Maintaining a list of equipment
The foundation of the entire maintenance and repair management system is the initial creation of a database of repair facilities and its further maintenance in the current state.
The main technical data of the equipment, information about its location, information about scheduled and emergency repairs are included in the equipment card. Regular record keeping in cards makes it possible to assess the technical condition of equipment, reasonably and accurately determine the annual need for replaceable elements (assemblies, units, devices) to replace worn out ones.
An important part of the description of serviced and repaired equipment, systems of buildings and structures, instrumentation and automation are multilevel equipment classifiers. The presence of a generally applicable classification in the system makes it possible to structure homogeneous information about equipment, carry out typing, and quickly search for the necessary equipment groups and standards.
The system implements the ability to automatically create a hierarchical list of equipment for a given attribute of the repair object.
The classifier of normative maintenance and repairs contains complete information about all possible repairs and maintenance specified for the types, models and groups of equipment in the enterprise. This classifier includes information on routings of maintenance and repairs. The ability to maintain classifiers for both fixed repair cycles and for successive chains of related repairs has been implemented.
The maintenance and repair workflow contains a list of elementary maintenance and repair operations with an indication of the standard MTO costs and labor costs for each operation. The system supports versioning of technological maps.
Implemented the ability to reflect the operations of acceptance for accounting and write-off of equipment.
Performance Management
· Accounting for equipment inspections.
· Accounting for controlled indicators.
· Logging of defects.
· Accounting operating time.
· Accounting for equipment conditions.

Accounting for equipment conditions
Operational (maintenance and repair) personnel conduct inspections of equipment assigned to it during the reception and delivery of shifts.
All defects discovered during inspections: malfunctions in the equipment, deviations from the normal state of the equipment, including those that do not require an immediate stop to eliminate them, are recorded in the system in the Defect Log.
Separately, it is necessary to highlight technical inspections of equipment. They are a special case of regulated maintenance, are planned along with repairs.
In the process of equipment inspections, the values \u200b\u200bof monitored indicators are measured and entered into the system. When critical values \u200b\u200bare reached, personnel generate a notice of the need for repairs. The system implements the ability to configure automatic distribution of notifications to responsible persons and automatically enter documents about detected defects when critical values \u200b\u200bare reached.
Keeping a history of the readings of measuring instruments allows you to track the current status of the equipment.
Depending on the production significance of the equipment, the effect of its failures on the safety of personnel and the stability of production and technological processes, repair actions can be implemented in the form of overhaul repair, repair in technical condition, or in the form of a combination thereof. In the system, you can plan repairs for all of the above strategies. In fact, the repair of most of the equipment is inevitably based on a combination (in various proportions) of the regulated repair and repair over time.
The operating time of the equipment can be expressed in machine hours, kilometers of run, cubic meters of excavated rock, liters, etc. The operating time of the equipment is recorded in the system in the Operating Journal.
The system implements the ability to keep records of equipment in various conditions: in repair, conservation, emergency downtime. Based on the data recorded in the system, it is possible to quickly obtain information on equipment downtime for a given period, and calculate the efficiency indicators of equipment use.
Maintenance and repair planning
· Formation of schedules for PPR equipment.
· Formation of applications for repairs.
· Planning the need for spare parts, materials and tools.
· Planning labor requirements.
· Budgeting for repairs.
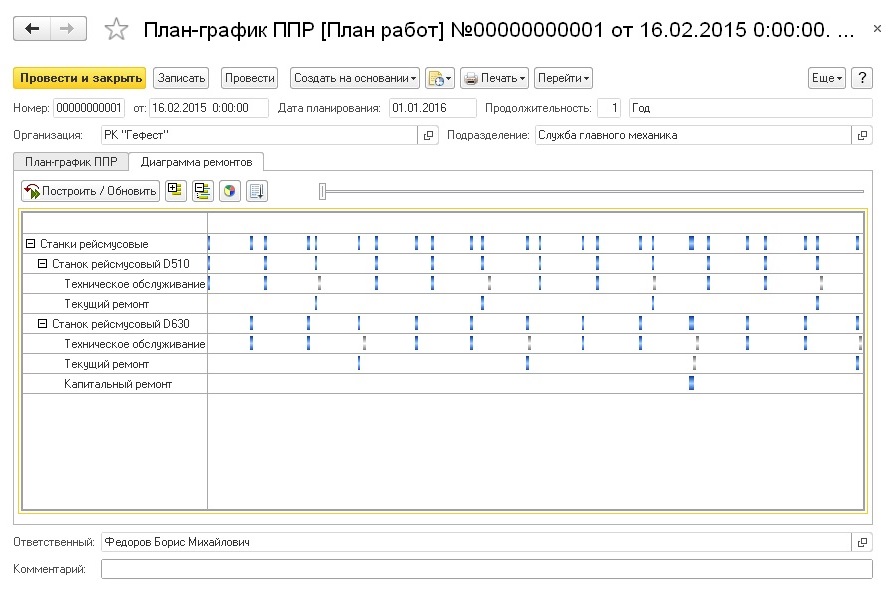
Formation of schedules for PPR equipment
The basic purpose of creating the schedules for equipment maintenance is to ensure the proper safety of the equipment in the long term, that is, to maintain the standard level of its technical condition and operability.
Based on the basic goal, specific targets and indicators are formed, the most important tasks for maintenance and equipment repair are justified and solved:
- the formation of long-term, annual and monthly repair plans;
- development of key areas and priorities;
- determination of the need for types and volumes of work for each object;
- determination of the main sources of resource supply and ways to attract the necessary resources.
Annual schedules of PPR equipment are compiled in the system by the mechanics of units, which previously coordinate them with other services of the enterprise. The annual schedule of PPR includes all equipment to be repaired in the planned year, as well as regulated maintenance. Based on the annual PPR schedules with the help of special adjustment documents, it is possible to generate annual, monthly and weekly PPR schedules. When they are formed, the system takes into account actual data on the repair objects recorded in the system.
Based on the PPR schedule, the system generates repair estimates (repair requests), which are operational documents for planning repair work.
The need for spare parts, materials and tools in the system is formed from the composition of the technological operations of standard maintenance and repairs as part of the PPR schedule.
In accordance with the functions performed, the number of repair personnel is determined. The total number of repair workers necessary for the upcoming repair is determined in the system by the number of equipment to be repaired, the complexity of the repair of each piece of equipment, the duration of the repair and the accepted mode of repair work at the enterprise (number of shifts, their duration).
In order to formulate a budget for a certain period, PPR schedules for this period should be formed. Based on information about planned regulatory maintenance and repairs, the amount of prospective costs is calculated.
Repair Logistics Management
· Maintaining primary accounting of MTO.
· Control of the minimum balance.
· Recalculation of planned costs.
· Formation and control of the implementation of orders for domestic consumption.
· MTO cost control.

MTO cost control
The initial accounting of the MTO as part of the maintenance and repair management is to determine the list of the MTO nomenclature used when performing maintenance and repairs.
The system implements the ability to set the minimum balance - the minimum number of MTOs that must always be in stock in case of emergencies: accidents, breakdowns requiring unscheduled repairs, etc. The minimum MTO balance can be written off only in the event of an emergency.
For the possibility of changes in repair plans for a certain period, the system has implemented the ability to adjust the planned costs of the MTO.
Based on the need for materials in the system, applications (orders for domestic consumption) for its provision are compiled, which are subject to further processing in the department of material and technical support (MTO) of the enterprise.
Based on an internal consumption order, item items can be reserved from the current stock balance or placed in orders with suppliers.
To control MTO costs, the planned and actual indicators of item costs in quantitative and monetary terms are compared. Planned indicators in the system are formed on the basis of the PPR schedules for the required period, as well as those formed on the basis of them and on the basis of defects and external reasons for the repair estimates. Actual indicators are formed on the basis of acts of work performed.
Personnel Management
· Definition of required competencies.
· Formation of a list of employees.
· Control of labor costs.
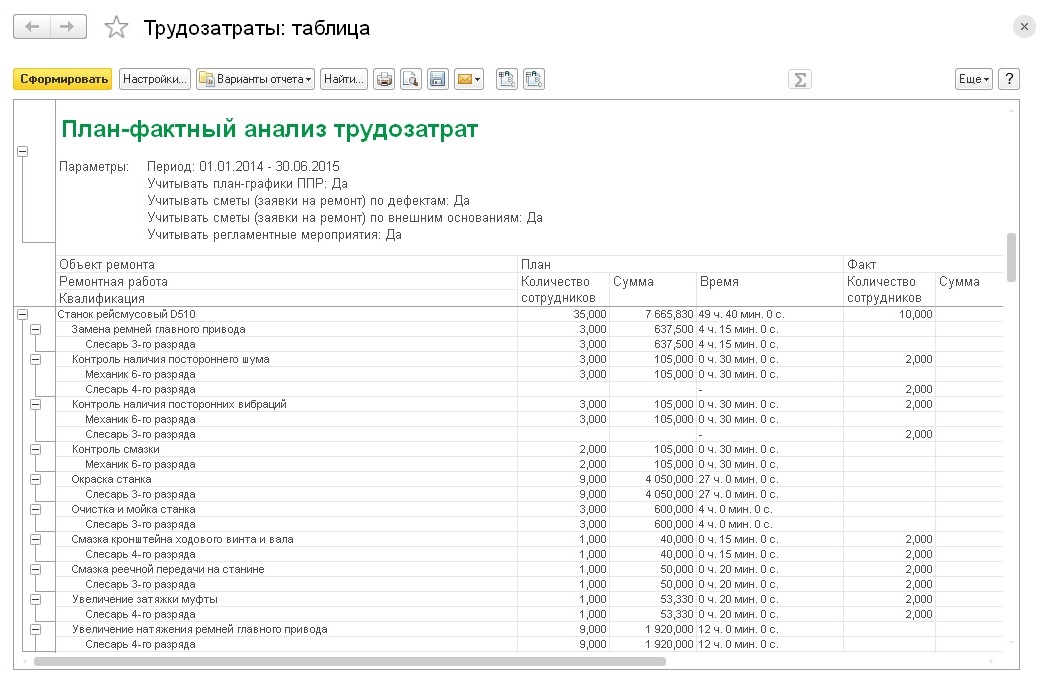
Labor control
To ensure the continued operability of equipment at the enterprise, the system implements tools for regulating the number of repair personnel.
The definition of the necessary competencies in the framework of maintenance and repair management is to determine the list of qualifications required when performing maintenance and repairs.
After determining the list of qualifications required for maintenance and repair, it is necessary to assign a correspondence between qualifications and employees performing maintenance and repairs.
When planning labor costs, the required number of repair workers required to perform certain operations is compared with the amount available at the enterprise. Based on the results of this analysis, decisions can be made on managing the number of personnel and their performance.
To control labor costs, the system provides the ability to compare planned and actual costs in quantitative and monetary terms. Planned indicators are formed on the basis of the PPR schedules, as well as those formed on their basis and on the basis of defects and external bases for the repair estimates, for the required period. Actual indicators are formed on the basis of acts of work performed.
Management of orders and work
· Registration and processing of unscheduled requests for repairs.
· Formation and control of orders for repair work.
· Preparation of outfit tolerances.
· Accounting for work performed.
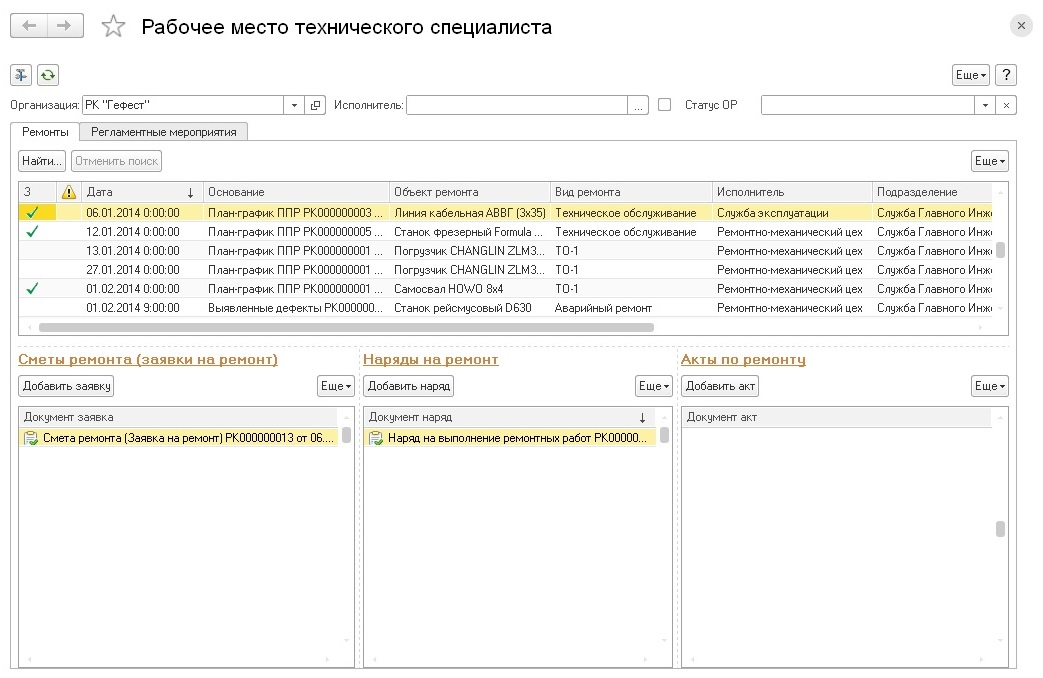
Accounting for work performed
The purpose of the management of work orders and work is the formation and accounting of the execution of work orders for repair work, if necessary, the formation of work orders, approvals for them, as well as the account of repair work performed.
Based on the generated repair requests, it is possible to form work orders for repair work in the system.
Measures to ensure the safe conduct of repair work are determined and executed immediately before the start of repair in the form of a permit, which is an admission order for conducting fire, gas hazardous and other works in accordance with current instructions.
The completion of repair work is documented by the act of completion.
Document Management
· Storage of historical data on equipment repairs.
· Maintaining a database of text and graphic documents.

Storage of historical equipment repair data
The purpose of the documentation management is to provide repair service personnel with quick access to the necessary documents and the history of equipment repairs.
Information on scheduled and emergency repairs is recorded in the system in chronological order on the equipment card. Regular record keeping in cards makes it possible to assess the technical condition of the main equipment, reasonably and accurately determine the annual need for replaceable elements (units, assemblies, devices) to replace worn out ones.
The system provides the ability to maintain a database of text and graphic documents. The database of documents allows you to perform the following actions:
- input, adjustment and display of text and graphic documents (including tables, diagrams, drawings and photographs);
- binding documents to pieces of equipment.
The system has the ability to configure integration in the system “1C: Document Management“.
Performance analysis and reporting
· Reporting on performance indicators.
· Formation of other reporting.
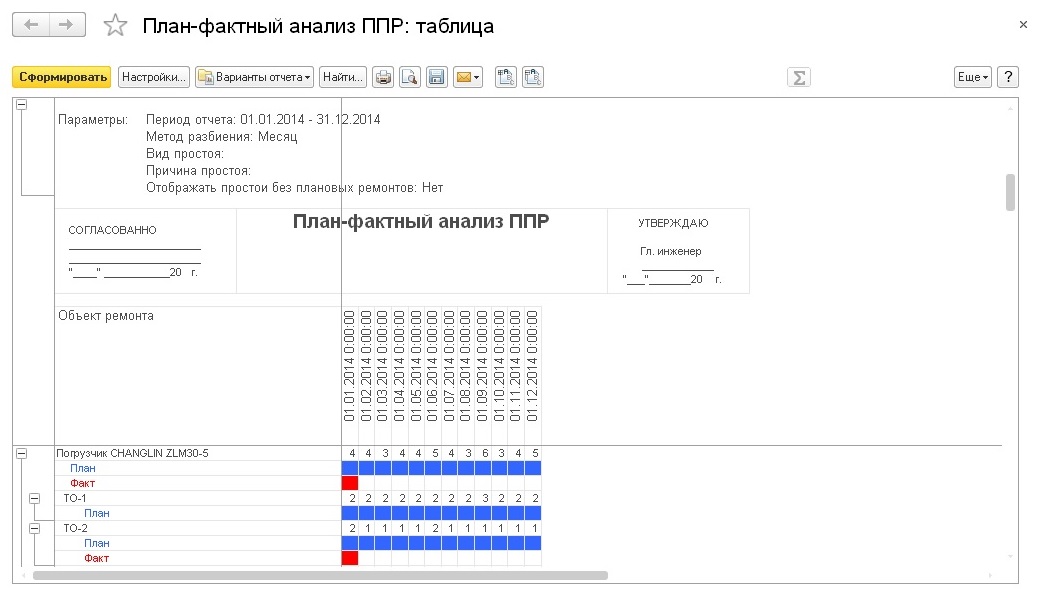
Reporting on performance indicators
To analyze the effectiveness of asset management in the system, you can use the following reports:
· Plan-factual analysis of PPR.
· Plan-factual cost analysis.
· Nomenclature costs.
In addition, depending on the functions performed, the employee can generate various reports:
· List of equipment.
· Operating time equipment.
· Controlled indicators.
· Stand down equipment.
· MTO plan, labor costs and tools.
· The plan-fact of the implementation of repairs by contractors and others.
The system implements the ability to configure scheduled tasks for sending reports to responsible persons. It is possible to use different report settings when generating distributed reports to various responsible ones.
Technological advantages
"1C: TOIR Maintenance and repair management of equipment 2 KORP" was developed on the latest version of the technological platform "1C: Enterprise 8.3", which allows you to:
- provide high reliability, performance and scalability of the system;
- organize work with the system via the Internet, in the thin client or web client mode (through a regular Internet browser), including in the "cloud" mode;
- create mobile jobs using tablets and smartphones running iOS or Android;
- configure the interface for a specific user or group of users, taking into account the role of the user, his access rights and individual settings.
The mechanism of functional options implemented in "1C: MRO Maintenance and repair of equipment 2 KORP" allows you to "enable" or "disable" the various functional parts of the application solution without programming (configuration changes).
The software product is intended for specialists in the organization of repairs and maintenance of industrial equipment, as well as for all departments related to asset management, repairs and maintenance: finance and accounting, logistics and supply, personnel management.
Main users "1C: TOIR":
- Chief Mechanic Service,
- Chief Power Engineer Service,
- Service of Instrumentation, Automated Process Control Systems,
- Service of the chief metrologist.
Product Highlights “1C: Enterprise 8. MRO Management of repairs and maintenance of equipment”:
- Formation of a real budget for equipment maintenance and repair.
- High level of planning, optimization of costs and work.
- "Transparency" of the work of all departments.
- Effective use of enterprise assets at all stages of their life cycle - from acquisition or planning and creation, to decommissioning or sale.
- The ability to keep a quality record of costs and reliability for each piece of equipment.
- Automatic scheduling of scheduled repairs and maintenance, generation of work orders.
- Opportunities for scheduling services of MTO schedules of real needs and supplies.
- Improving discipline among technology services.
- Increase in the final profit of the enterprise.
Software “1C: Enterprise 8. MRO Management of repairs and maintenance of equipment” improves the efficiency of various services of enterprises:
- enterprise management and managers responsible for business development: ample opportunities for analysis, planning and flexible management of enterprise resources to increase competitiveness, ensuring “transparency” of production assets;
- heads of departments, managers and employees directly involved in production, marketing, supply and other activities to ensure the production process: tools to improve the efficiency of daily work in their areas;
- repair workers: the ability to use products as the basis for work management - an archive of all regulatory and technical documentation, PPR schedules are calculated, orders for repair work are written out, a record of repair work is kept;
- employees of accounting services of the enterprise: tools for automated accounting in full compliance with legal requirements and corporate standards of the enterprise.
Program "1C: TOIR" can significantly reduce the cost of maintenance and repairs, reduce the downtime of equipment, increase its load. Such results are achieved due to the following factors:
- A huge amount of technical documentation (hundreds of thousands, not rarely millions of pages of descriptions) is processed automatically - the accuracy and reliability of planning and accounting are significantly increased, and the requirements of supervisory authorities are met.
- Scheduled maintenance is cheaper (compared to emergency), the number of emergency repairs and purchases is reduced.
- The MTO process is optimized on the basis of accurate data: the rejection of “expensive” equipment in operation, the reduction of stocks
- Transfer of a part of equipment for repair as
- Personification of responsibility, control over personnel qualifications
- Calculation of costs according to norms, and not “like last year + inflation”, (there have been cases of cost reductions of 50%!)
- Deciding on the fate of an asset based on full information
- Reduce equipment downtime.
The software product can be used both at individual enterprises and in production holding companies to ensure the unification of production and regulated accounting of repairs.
When developing a configuration "1C: Enterprise 8. MRO Management of repairs and maintenance of equipment”Took into account both modern international enterprise management techniques (EAM, CMMS, MRP II, CRM, SCM, ERP, etc.), as well as the experience of successful enterprise automation gained by 1C and the partner community. The system is used at industrial facilities with the most stringent requirements of Gosgortekhnadzor (for example, in petrochemicals), as well as at enterprises of the first category of explosive and fire hazard, including AES Ekibastuz LLP, MAEK Kazatomprom.
Licensing
Attention! To scale and expand the number of jobs, you can purchase additional licenses.
Functional Description
“1C: Enterprise 8. MRO Management of repairs and maintenance of equipment” includes the following main functions:
- Maintenance of reference information
Allows you to maintain the structure of the enterprise’s funds in the form of a tree, starting from the enterprise itself, site, workshop, installation, equipment and assembly. This type of presentation provides maximum visibility of the entire structure of the enterprise’s assets and a convenient type of work with the system.
- Maintaining equipment passports
The equipment passport contains all the necessary information, including the ability to visualize technical documentation.
The system reflects the organizational structure of the repair services of the enterprise. For example, the services of the chief mechanic, chief power engineer and metrologist. The direct executors of repairs and their categories are indicated. The availability of labor resources is determined as the entire volume of repair work, as well as the cost of labor resources. This information is important for budgeting and monitoring its implementation.
The system provides for the maintenance of typical repairs, hours of work, methods of performing repairs, types of repairs, units of measurement (counters), measured indicators, warehouses, manufacturers, repair contractors, types of defects, equipment conditions, materials.
- Schedule repairs
The repair schedule is formed on the basis of a given repair cycle, both by unit of equipment and by installation, site, or the entire enterprise.
- Keeping work orders
All repair work is carried out on work orders. Outfits are generated automatically, along with all the necessary documentation for the repair. The system allows you to track the performance of work by orders, take into account the implementation of part of the work. The package of documents includes all applications for materials, which increases management efficiency.
- Formation of the need for MTO
The decisions automatically generate a report on the need for MTO for a year, a planned schedule, as well as a schedule for each month, with the possibility of adjustment.
- Optimization of repair costs
When scheduling repairs, equipment downtime for equipment complexes is automatically minimized, thereby reducing the cost of time losses. Due to the convenience of analyzing the cost of ownership of equipment (purchase price, cost of maintenance and downtime), you can choose the best equipment for the purchase.
The greatest effect from the use of this software product is achieved when integrating with a standard configuration "1C: Production Enterprise Management 8" . Integration instructions are given in the book “1C: Enterprise 8. MRO Maintenance and repair of equipment. User Guide ”included in the package.
Licensing Features
Software “1C: Enterprise 8. MRO Management of repairs and maintenance of equipment” provides the application solution at one workplace at one time.To work in multi-user mode, users must have configuration licenses “1C: TOIR Maintenance and repair of equipment”and client licenses 1C: Enterprise 8»For the appropriate number of jobs.
To work in client-server mode, users must have server licenses.
List of licenses
| Name | Cost | |
|---|---|---|
| 1C: TOIR Maintenance and repair of equipment. Client license for 1 workplace | 11 900 rub. |
Buy |
| 1C: TOIR Maintenance and repair of equipment. Client license for 5 workplaces | 54 000 rub. |
Buy |
| 1C: TOIR Maintenance and repair of equipment. Client license for 10 jobs | 96 000 rub. |
Buy |
| 1C: TOIR Maintenance and repair of equipment. Client license for 50 jobs | 324 000 rub. |
Buy |
| 1C: TOIR Maintenance and repair of equipment. Client license for 100 jobs | 480 000 rub. |
Buy |
|
1C: Enterprise 8. Client license for 1 workplace
|
6 300 rub. |
Buy |
|
1C: Enterprise 8. Client license for 5 workplaces
|
21 600 rub. |
During operation, process equipment is subject to physical and moral wear and tear and requires constant maintenance. The performance of the equipment is restored by repairing it. The technical basis for the need for repair is the unevenness of parts and components of technical means. It is technically impossible to make a machine, mechanisms, assembly with parts and assemblies of the same strength, uniform wear and about the same service life. Therefore, there is a need for maintenance and repair of equipment to ensure its normal operation for the entire guaranteed service life.
Repair and maintenance is of great economic importance to the enterprise. Studies show that the proportion of faulty equipment in different industries ranges from 3-5% to 10-15% or more, and this leads to large indicators of under-received products. The cost of repairing fixed assets in the cost of production reaches 6-14%.
Repairs(from Fr. remonter - correct, replenish, reassemble) - this is a set of operations to restore the health or working capacity of products or their components. It is produced when further operation of the equipment is impossible due to deterioration, breakdown, or before failure. In the first case, the method of restoring the technical condition was called "according to need" (technical condition); in the second - regulated repairs (scheduled - preventive).
In accordance with the nature of the work performed and the degree of restoration of the technical means, the following types of repair are distinguished:
- capital, the largest in volume and complexity, requires complete disassembly and repair of all basic parts, replacement of worn parts and assemblies, restoration of a certain part;
- middlerepairs are made to repair the malfunction by replacing or repairing parts that are worn out; partial disassembly of equipment is required;
- current repair - the minimum in terms of work, in which the restoration or replacement of worn parts and the regulation of mechanisms ensures the normal operation of the equipment until the next scheduled task.
Maintenance(TO) is a set of operations to maintain the operability or serviceability of a product (equipment) when used for its intended purpose, during storage and transportation.
There are such types of maintenance:
Periodic, performed through established operating time indicators or time intervals;
Regulated, provided in the normative - technical and operational documentation and carried out with frequency and established volumes, regardless of the technical condition at the time of the start of maintenance;
Seasonal, carried out to prepare the equipment for use in the autumn - winter and spring - summer conditions.
Maintenance can be scheduled if machines and equipment are installed on it in accordance with the requirements of normative - technical or operational documentation, and unscheduled - without prior appointment, to check the technical condition.
The technological element of maintenance and repair is diagnostics - a set of measures in the system of maintenance and repair, providing information on the status of equipment. Diagnostic tools carry out an in-depth check of the status of all mechanisms and systems of equipment, evaluate its performance indicators, identify malfunctions and provide control of the repair work.
All of these operations, together with other elements, form the basis of a preventive approach to maintaining equipment in working condition. The practical implementation of this approach is recognized around the world. system of preventive maintenance of equipment (PPR). It is a set of planned organizational and technical measures for the care, supervision of equipment, its maintenance and repair.
The PPR system is designed to provide:
Maintaining equipment in working condition and preventing accidents;
Possibility to carry out repair work according to the plan agreed with the production plan;
Timely preparation of spare parts and materials necessary for repair;
The rational organization of maintenance and repair of equipment;
Increase in the coefficient of technical use of equipment by improving the quality of repairs and reducing the downtime
The PPR system includes maintenance and scheduled repair of equipment, the essence of which is described above. The effectiveness of the system is largely determined by the development of its regulatory framework and the accuracy of established standards. The standards of the enterprise’s PPR system are differentiated by equipment groups. The main repair standards are repair cycles and their structure, categories of repair complexity, labor intensity and metal consumption of repair work, inventories for repair needs.
Repair cycle- this is the smallest repeating time interval or operating time of equipment during which all types of technological maintenance and repair are performed in a certain sequence. In other words, this is the operating time of the equipment from the start of its commissioning to the first overhaul or between two overhauls.
The quantity and sequence of the repairs and maintenance work included in the repair cycle is repair cycle structure, eg:
K– TO – T– TO  - T
- T  - TO – T– TO
- TO – T– TO  - K (6)
- K (6)
Where K - overhaul;
T, T  , T– current repairs;
, T– current repairs;
THAT THAT  etc. - Maintenance
etc. - Maintenance
The repair cycle is measured by the operational time of the equipment. The duration of the repair cycle is determined in used machine hours, depending on the service life of the main mechanisms and parts, the replacement or repair of which can be carried out during the complete dismantling of the equipment.
Overhaul period and the frequency of maintenance is also expressed by the number of hours worked (different units are used for cars and some other equipment).
The complexity and material consumption of repair and maintenance of equipment depend on its design features.
Repair difficulty category- represents the degree of complexity of equipment repair. It is determined by the number of repair complexity units assigned to this group of equipment by comparing it with the accepted standard - conditional equipment.
Repair unit - this is the complexity of the corresponding type of equipment repair of the first category of repair complexity.
